cho hình thoi ABCD có cạnh bằng a , có \(\widehat{BAD}=120^o\) , O là tâm của hình thoi . Tính độ dài vecto \(\overrightarrow{AD}-\overrightarrow{OC}\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Cho hình thoi ABCD cới cạnh có độ dài bằng 1 và \(\widehat {BAD} = {120^o}\). Tính độ dài của các vectơ \(\overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {CD} ,\;\overrightarrow {DB} + \overrightarrow {CD} + \overrightarrow {BA} .\)
Tham khảo:
\(\overrightarrow {CD} = \overrightarrow {BA} \) do hai vectơ \(\overrightarrow {CD} ,\;\overrightarrow {BA} \) cùng hướng và \(CD = BA\).
\(\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {CD} = \overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {BA} = \overrightarrow {CA} \\ \Leftrightarrow \left| {\overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {CD} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow {CA} } \right| = CA\end{array}\)
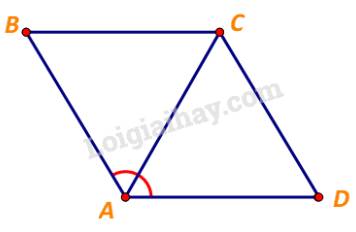
Xét tam giác ABC, ta có:
\(BA = BC\) và \(\widehat {BAC} = \frac{1}{2}.\widehat {BAD} = {60^o}\)
\( \Rightarrow \Delta ABC\) đều, hay \(CA = BC = 1\)
Vậy \(\left| {\overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {CD} } \right| = 1.\)
Dựa vào tính chất kết hợp, ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}\overrightarrow {DB} + \overrightarrow {CD} + \overrightarrow {BA} = \left( {\overrightarrow {DB} + \overrightarrow {CD} } \right) + \overrightarrow {BA} \\ = \left( {\overrightarrow {CD} + \overrightarrow {DB} } \right) + \overrightarrow {BA} = \overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {BA} = \overrightarrow {CA} .\\ \Rightarrow \left| {\overrightarrow {DB} + \overrightarrow {CD} + \overrightarrow {BA} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow {CA} } \right| = CA = 1.\end{array}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hình thoi ABCD tâm O, có cạnh bằng a, góc A 60 độ.
1. Tình \(\left|\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AD}\right|\)
2. Tính \(\left|2\overrightarrow{OB}-3\overrightarrow{OC}\right|\)
Cho hình bình hành ABCD có AB = 4, AD = 6, \(\widehat {BAD} = {60^o}\) (Hình 73).
a) Biểu thị các vecto \(\overrightarrow {BD} ,\overrightarrow {AC} \) theo \(\overrightarrow {AB} ,\overrightarrow {AD} .\)
b) Tính các tích vô hướng \(\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AD} ,\;\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} ,\;\overrightarrow {BD} .\overrightarrow {AC} .\)
c) Tính độ dài các đường chéo \(BD,AC.\)
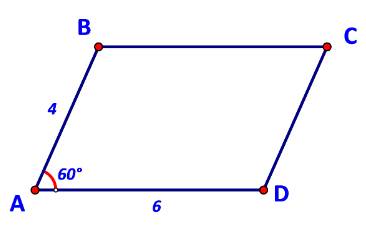
a) \(\overrightarrow {BD} = \overrightarrow {AD} - \overrightarrow {AB} ;\;\overrightarrow {AC} = \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} .\)
b) \(\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AD} = 4.6.\cos \widehat {BAD} = 24.\cos {60^o} = 12.\)
\(\begin{array}{l}\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} = \overrightarrow {AB} (\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} ) = {\overrightarrow {AB} ^2} + \overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AD} = {4^2} + 12 = 28.\\\overrightarrow {BD} .\overrightarrow {AC} = (\overrightarrow {AD} - \overrightarrow {AB} )(\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} ) = {\overrightarrow {AD} ^2} - {\overrightarrow {AB} ^2} = {6^2} - {4^2} = 20.\end{array}\)
c) Áp dụng định lí cosin cho tam giác ABD ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}\quad \;B{D^2} = A{B^2} + A{D^2} - 2.AB.AD.\cos A\\ \Leftrightarrow B{D^2} = {4^2} + {6^2} - 2.4.6.\cos {60^o} = 28\\ \Leftrightarrow BD = 2\sqrt 7 .\end{array}\)
Áp dụng định lí cosin cho tam giác ABC ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}\quad \;A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} - 2.AB.BC.\cos B\\ \Leftrightarrow A{C^2} = {4^2} + {6^2} - 2.4.6.\cos {120^o} = 76\\ \Leftrightarrow AC = 2\sqrt {19} .\end{array}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hình thoi ABCD đi có cạnh bằng a và có góc A bằng \(60^\circ \). Tìm độ dài của các vectơ sau: \(\overrightarrow p = \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} ;\overrightarrow u = \overrightarrow {AB} - \overrightarrow {AD} ;\overrightarrow v = 2\overrightarrow {AB} - \overrightarrow {AC} \).
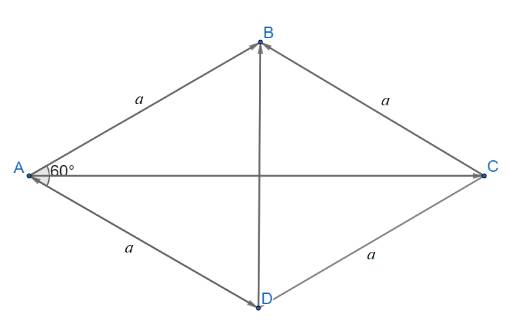
+) ABCD là hình thoi nên cũng là hình bình hành
Áp dụng quy tắc hình bình hành ta có:
\(\overrightarrow p = \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} = \overrightarrow {AC} \)
\(\Rightarrow |\overrightarrow p| = | \overrightarrow {AC}| =AC \)
+) \(\overrightarrow u = \overrightarrow {AB} - \overrightarrow {AD} = \overrightarrow {DB} \)
\(\Rightarrow |\overrightarrow u| = | \overrightarrow {DB}| =DB\)
+) \(\overrightarrow v = 2\overrightarrow {AB} - \overrightarrow {AC} = \overrightarrow {AB} + \left( {\overrightarrow {AB} - \overrightarrow {AC} } \right) = \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {CB} \)\( = \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {DA} = \overrightarrow {DB} \)
\(\Rightarrow |\overrightarrow v| = | \overrightarrow {DB}| =DB\)
+ Tính \(AC, DB\)
Tam giác ABD có \(AB=AD=a, \widehat A = 60^o\) nên nó là tam giác đều. Do đó DB = a.
Gọi O là giao điểm hai đường chéo.
Ta có: \(AO = AB. \sin B = a. \sin 60^o = \frac {a \sqrt 3}{2} \Rightarrow AC = a \sqrt 3\)
Vậy \(|\overrightarrow p| = a \sqrt 3 ,|\overrightarrow u| = a, |\overrightarrow v| = a.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hình vuông ABCD có cạnh a. Tính độ dài các vecto sau:
a) \(\overrightarrow {DA} + \overrightarrow {DC} \)
b) \(\overrightarrow {AB} - \overrightarrow {AD} \)
c) \(\overrightarrow {OA} + \overrightarrow {OB} \) với O là giao điểm của AC và BD.
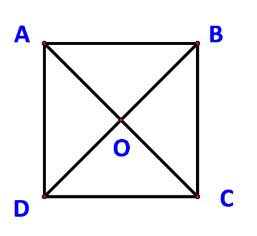
a) Do ABCD cũng là một hình bình hành nên \(\overrightarrow {DA} + \overrightarrow {DC} = \overrightarrow {DB} \)
\( \Rightarrow \;|\overrightarrow {DA} + \overrightarrow {DC} |\; = \;|\overrightarrow {DB} |\; = DB = a\sqrt 2 \)
b) Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {AD} + \overrightarrow {DB} = \overrightarrow {AB} \) \( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {AB} - \overrightarrow {AD} = \overrightarrow {DB} \)
\( \Rightarrow \left| {\overrightarrow {AB} - \overrightarrow {AD} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow {DB} } \right| = DB = a\sqrt 2 \)
c) Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {DO} = \overrightarrow {OB} \)
\( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {OA} + \overrightarrow {OB} = \overrightarrow {OA} + \overrightarrow {DO} = \overrightarrow {DO} + \overrightarrow {OA} = \overrightarrow {DA} \)
\( \Rightarrow \left| {\overrightarrow {OA} + \overrightarrow {OB} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow {DA} } \right| = DA = a.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
cho hình thoi ABCD cạnh bằng a có tâm O, góc BAD =60 ĐỘ. tính độ dài vec tơ sau.
a) VECTO AB + VECTO AD.
b) VECTO AB - VECTO AC.
c)VECTO AB + VECTO AC.
d) VECTO AD + VECTO CB.
e) VECTO OB - VECTO DC
Cho hình thang ABCD có \(\overrightarrow{2AB}=\overrightarrow{DC}\),AC=8,BD=6,góc tạo bởi 2 vecto \(\overrightarrow{AC}\) và \(\overrightarrow{BD}\) bằng 120.Tính độ dài các cạnh AD,BC
Cho hình thoi ABCD cạnh a, \(\widehat{BCD}\)= 60o . O là giao điểm của AC và BD . Tính \(\left|\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AD}\right|,\left|\overrightarrow{CB}+\overrightarrow{DC}\right|\)
Cho hình thoi abcd Tâm o cạnh a góc BAD Bằng 60 °. Gọi I J lần lượt là trung điểm AB , CD Và K Là trung điểm của I J.
a. CMR: Ka + Kb + Kc + Kd = 0
b. Tính độ dài Vecto AB + AD










